Casting Classification
1.Sand Casting
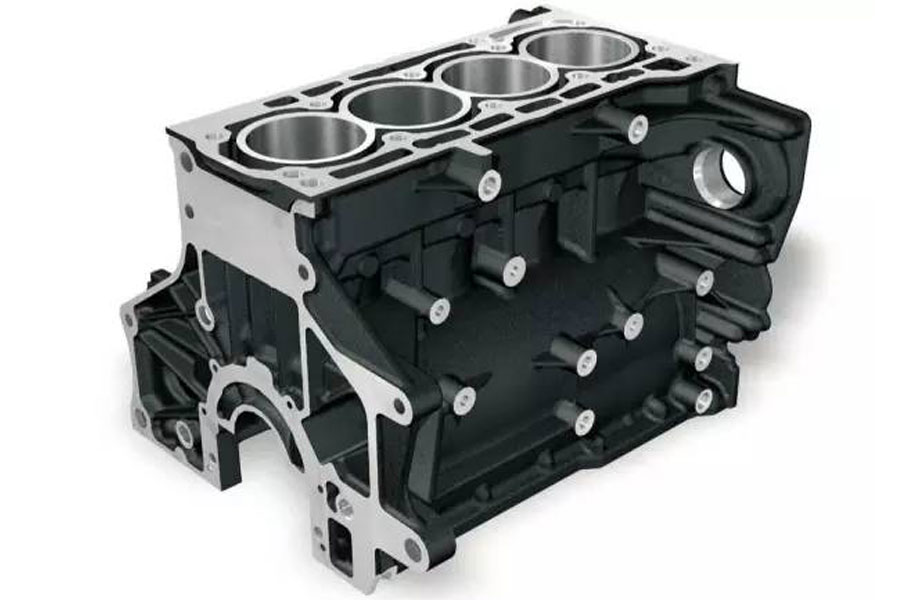

Sand casting: A casting method for producing castings in sand. Steel, iron and most non-ferrous alloy castings can be obtained by sand casting methods.
Process flow:
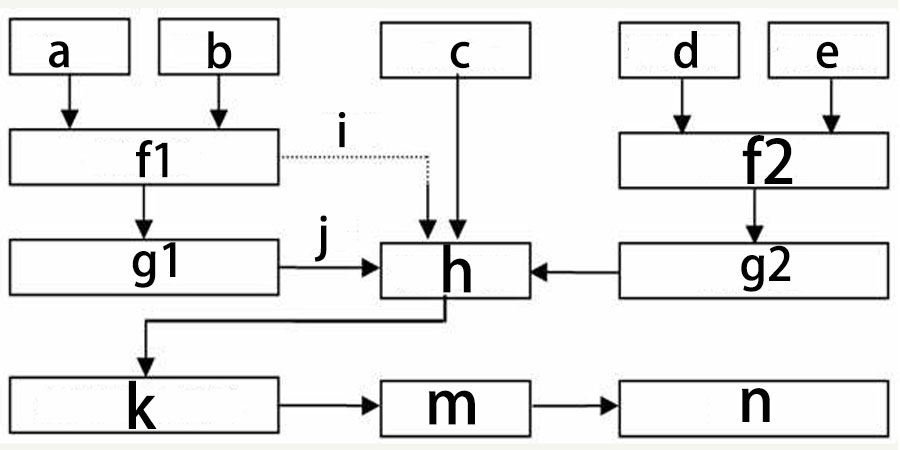
Technical Features:
2.Investment Casting
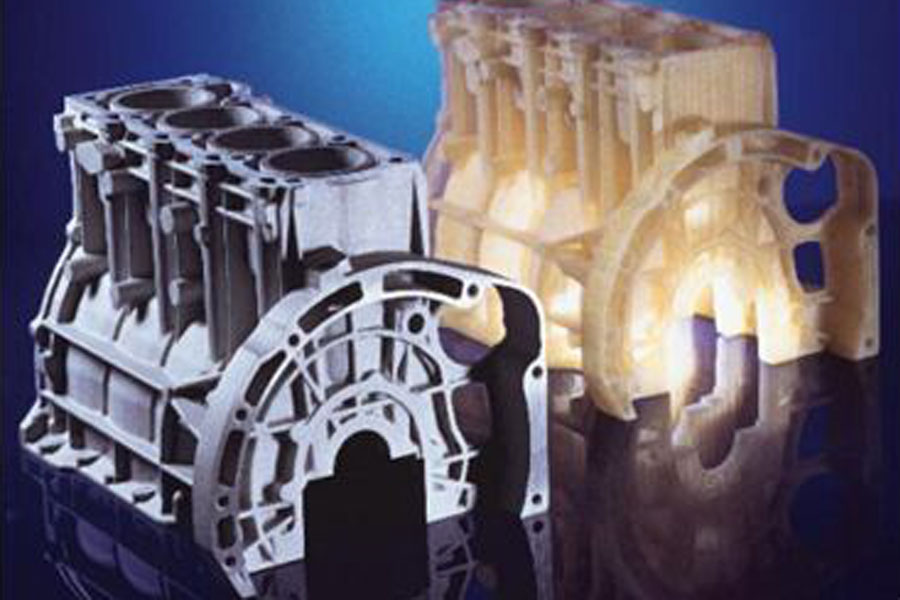

Investment casting: usually refers to making a pattern made of fusible materials, covering the surface of the pattern with several layers of refractory materials to form a shell, and then melting the pattern out of the shell to obtain a mold without a parting surface. After high temperature baking Then, it can be filled with sand and poured. Often referred to as "lost wax casting".
Process characteristics advantage:
Disadvantages: complicated procedures and high cost
Application: Suitable for the production of small parts with complex shapes, high precision requirements, or other processing difficulties, such as turbine engine blades.
3.Die Casting
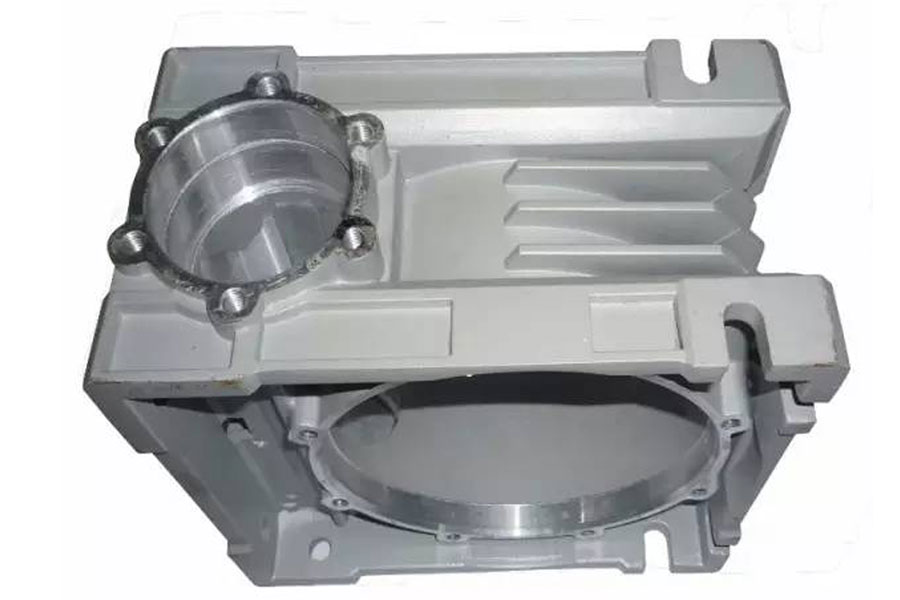

Die casting: It uses high pressure to press molten metal into a precision metal mold cavity at high speed. The molten metal is cooled and solidified under pressure to form a casting.
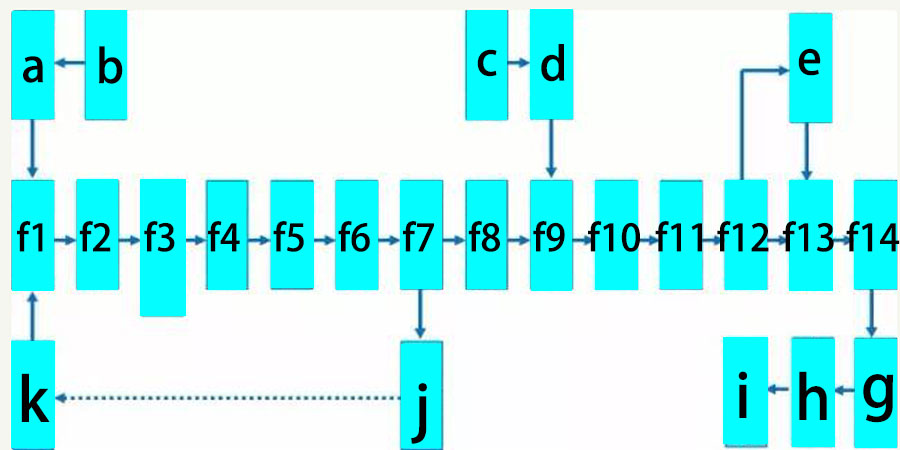
Die Casting Process:
Process characteristics
advantage:
Disadvantages:
Application: Die castings were first used in the automobile industry and instrument industry, and later gradually expanded to various industries, such as agricultural machinery, machine tool industry, electronics industry, defense industry, computer, medical equipment, clocks, cameras, and daily hardware, etc. .
4.Low Pressure Casting

Low pressure casting: refers to the method of filling the mold with liquid metal under lower pressure (0.02~0.06MPa) and crystallizing under pressure to form castings.
Technical features:
Application: Mainly traditional products (cylinder head, wheel hub, cylinder frame, etc.).
5.Centrifugal Casting
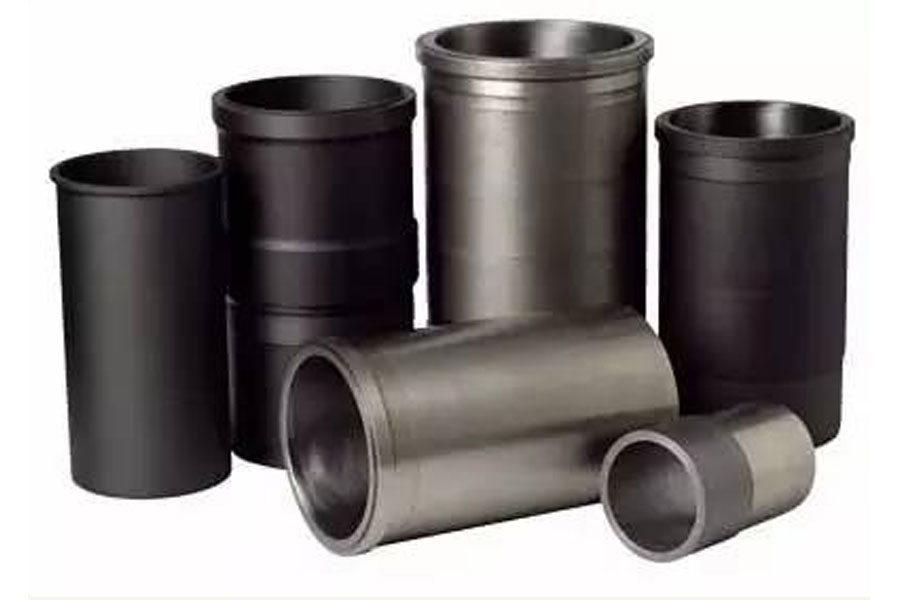

Centrifugal casting: is a casting method in which molten metal is poured into a rotating mold, and the mold is filled under the action of centrifugal force to solidify and shape.
Process characteristics
advantage:
Disadvantages:
application:
Centrifugal casting was first used in the production of cast pipes. At home and abroad, centrifugal casting was used in metallurgy, mining, transportation, irrigation and drainage machinery, aviation, national defense, automobile and other industries to produce steel, iron and non-ferrous carbon alloy castings. Among them, the production of castings such as centrifugal cast iron pipes, internal combustion engine cylinder liners and shaft sleeves is the most common.
6.Gravity Die Casting
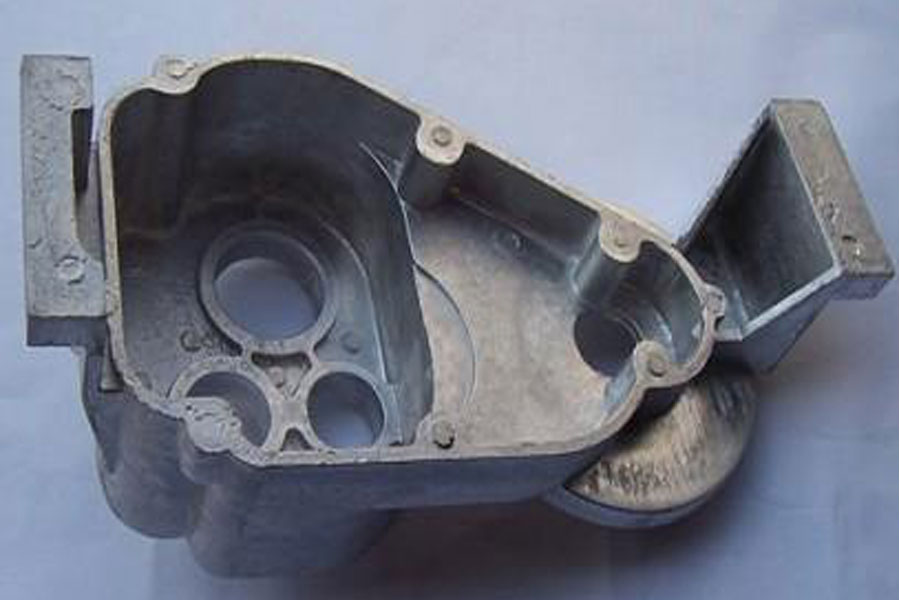

Gravity Die Casting: refers to a molding method in which liquid metal is filled with a metal mold under the action of gravity and cooled and solidified in the mold to obtain a casting.
Process characteristics
advantage:
Disadvantages:
Application: Metal mold casting is not only suitable for mass production of non-ferrous alloy castings such as aluminum alloys and magnesium alloys with complex shapes, but also suitable for the production of iron and steel metal castings and ingots.
7.Vacuum Die Casting
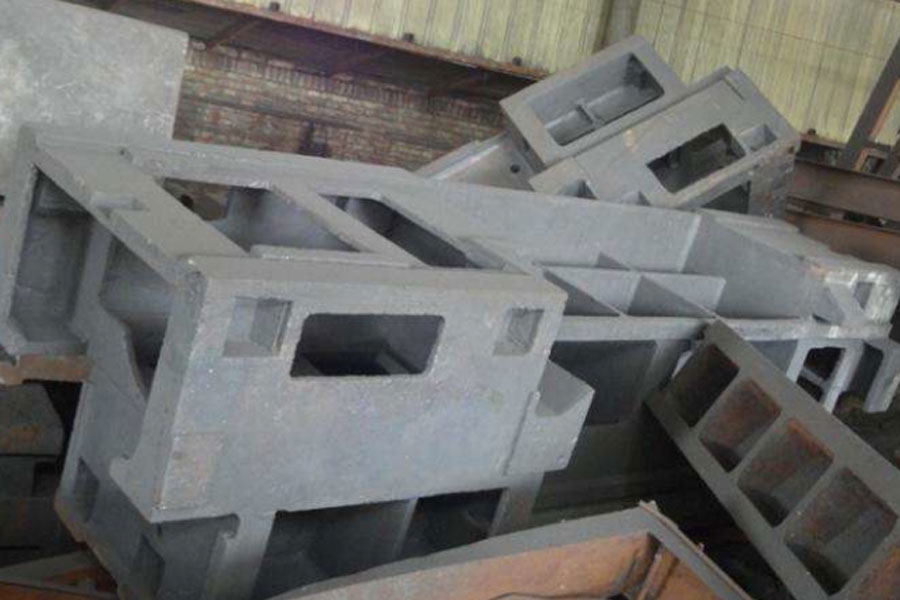

Vacuum casting: An advanced die-casting process that eliminates or significantly reduces the pores and dissolved gases in the die-casting parts by removing the gas from the die-casting mold cavity during the die-casting process, thereby improving the mechanical properties and surface quality of the die-casting parts.
Process characteristics
advantage:
Disadvantages:
8.Squeezing Die Casting

Squeeze casting: is a method of solidifying, flowing and forming liquid or semi-solid metal under high pressure to directly obtain parts or blanks. It has the advantages of high utilization rate of liquid metal, simplified process and stable quality. It is an energy-saving metal forming technology with potential application prospects.
Technical features:
Application: It can be used to produce various types of alloys, such as aluminum alloy, zinc alloy, copper alloy, ductile iron, etc.
9.Lost Foam Casting
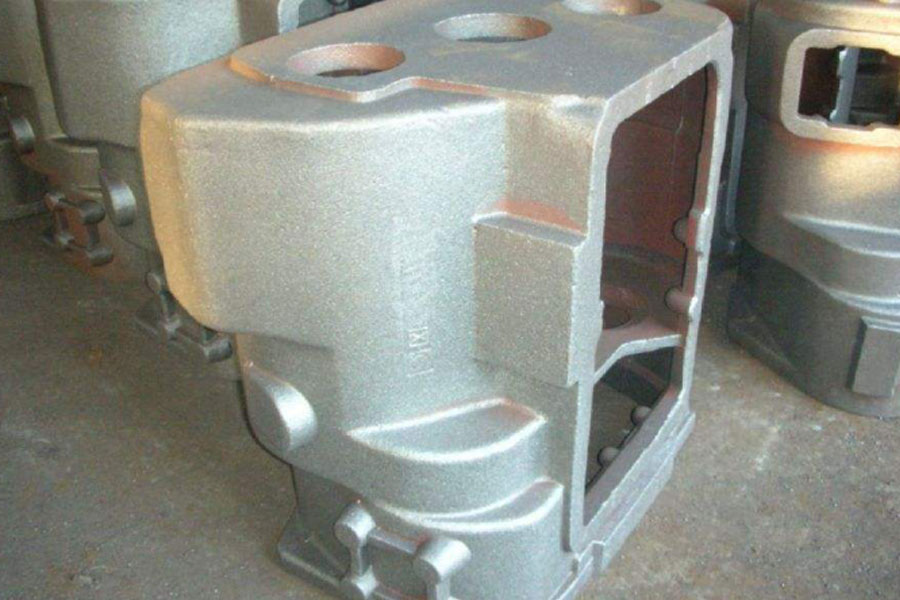

Lost foam casting (also known as full mold casting): It is to combine paraffin wax or foam models with similar size and shape to the castings to form clusters. After brushing and drying refractory coatings, they are buried in dry quartz sand for vibration modeling. It is a new type of casting method in which the mold is vaporized by pouring under pressure, the liquid metal occupies the position of the mold, and the casting is formed after solidification and cooling.
Process flow: pre-foaming→foaming→dipping coating→drying→modeling→pouring→falling out→cleaning
Technical features:
Application: It is suitable for the production of precision castings of various sizes with complex structures, unlimited types of alloys, and unlimited production batches. Such as gray cast iron engine box, high manganese steel elbow, etc.
10.Continual Casting
Continuous casting: It is an advanced casting method. Its principle is to continuously pour molten metal into a special metal mold called a mold. The solidified (crusted) castings are continuously removed from the mold. Pull out one end, it can get any length or specific length casting.
Continuous Casting Process:
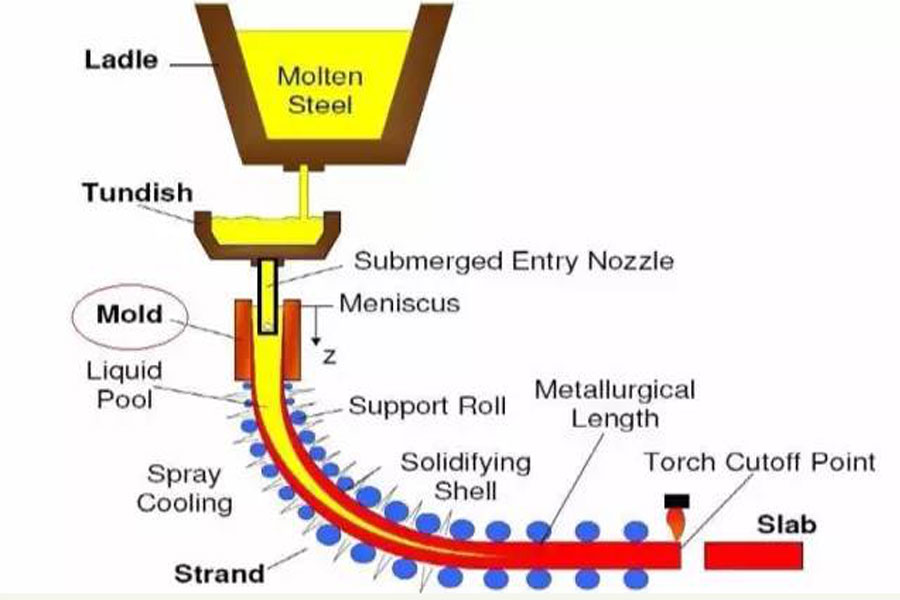
Technical features:
Application: Continuous casting can be used to cast steel, iron, copper alloys, aluminum alloys, magnesium alloys and other long castings with constant cross-sectional shapes, such as ingots, slabs, billets, tubes, etc.









